Qt and Trivial Relocation (Part 3) -- Giuseppe D'Angelo
![]() In the last post of this series we started exploring how to erase an element from the middle of a vector.
In the last post of this series we started exploring how to erase an element from the middle of a vector.
Qt and Trivial Relocation (Part 3)
by Giuseppe D'Angelo
From the article:
The reference semantics backstab
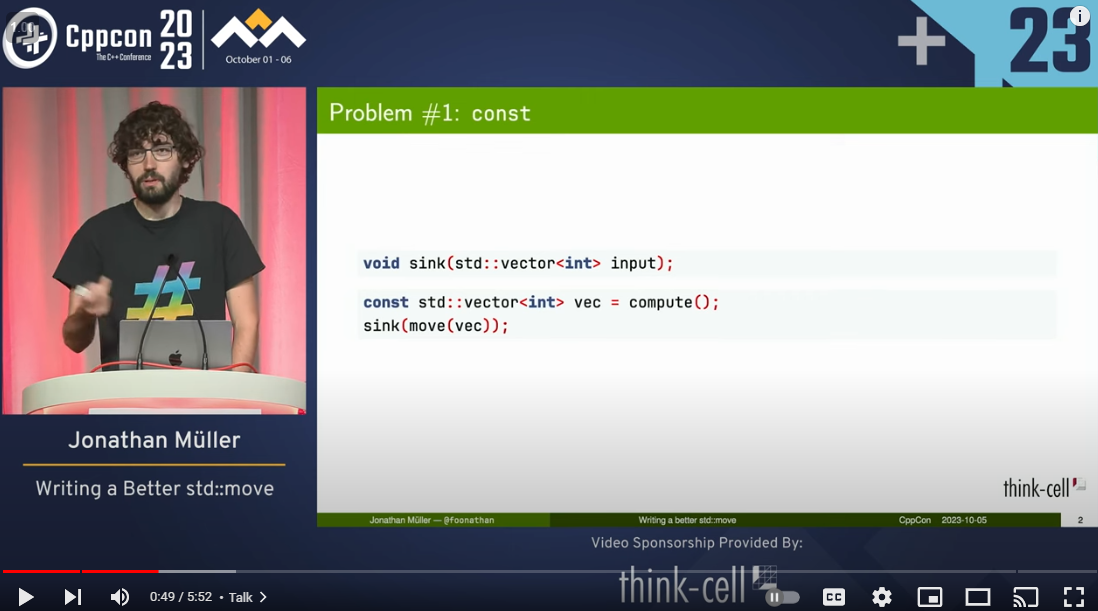
Let’s start by analyzing erase()‘s behavior once more.
Do you remember our claim that the specific strategy used does not really matter; that is, that they are all equivalent? Well, not so fast! It is actually quite imprecise to say that they are all equivalent.
They may be, as long as we deal with types which have value semantics. If we instead use a type that has reference semantics, the choices are absolutely not equivalent, and will yield different outcomes. This is because the semantics of assignment for (certain) reference types are write-through: they assign through the reference (instead of rebinding the reference).
Since we are implementing erasure in terms of assignments (or swaps, which boil down to assignments), this means that the precise sequence of operations done by erase will be visible due to its side-effects; and it also means that changing the strategy will produce different outcomes!